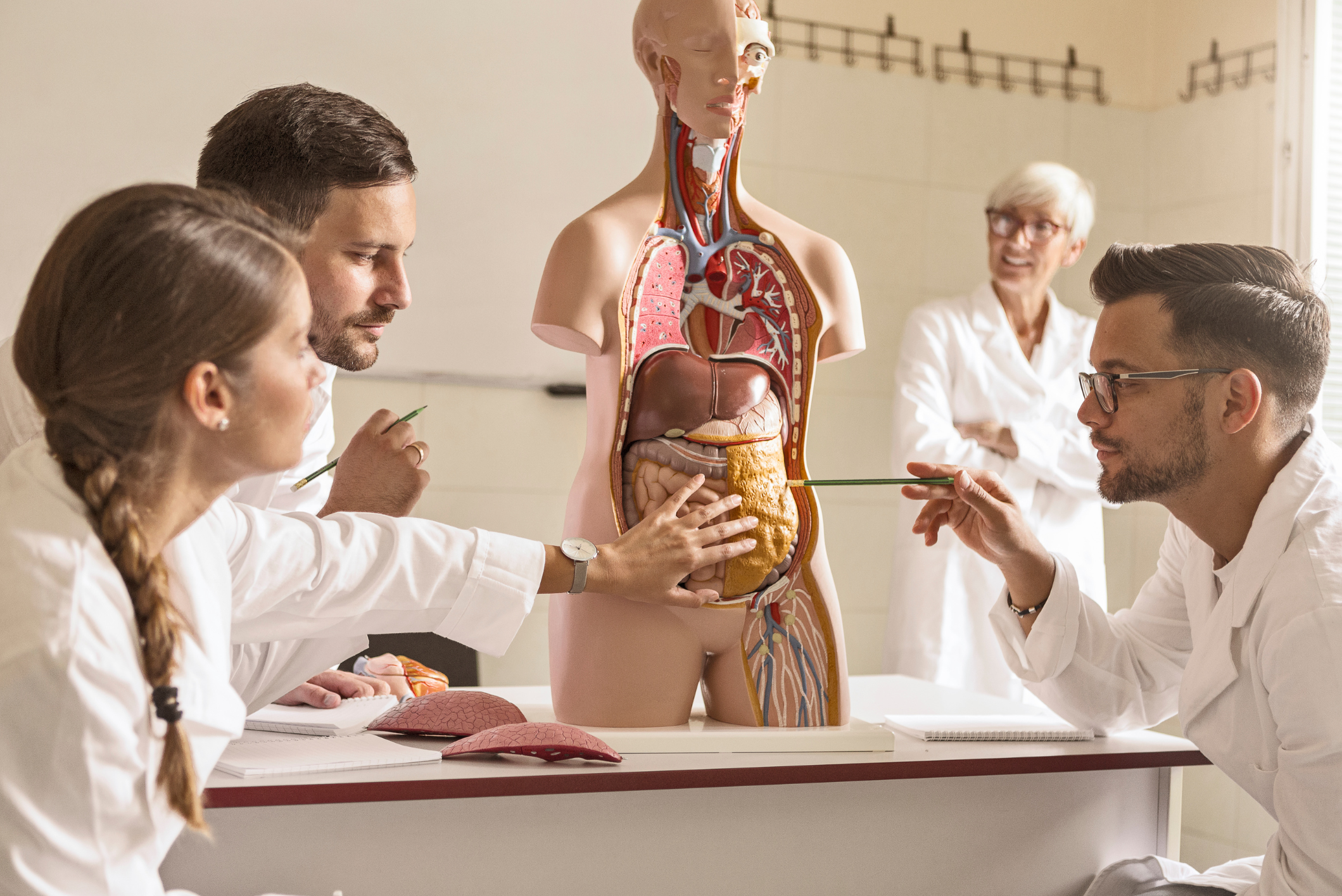
Medical coding requires more than just an understanding of codes and guidelines; it demands a solid grasp of human anatomy. Accurate coding hinges on knowing the body's structures and how they relate to specific diagnoses, procedures, and services. In this blog, we’ll explore the key areas of anatomy that every medical coder should focus on to ensure precise and effective coding.
1. Cardiovascular System: The Heart of Coding
The cardiovascular system is one of the most critical areas for coders, given the prevalence of heart-related conditions and procedures. Understanding the anatomy of the heart, including the atria, ventricles, valves, and major blood vessels like the aorta and coronary arteries, is essential. Coders must be able to identify and differentiate between conditions such as myocardial infarctions, heart valve disorders, and arrhythmias, as well as accurately code for procedures like angioplasty, stent placement, and bypass surgery.
Key Anatomy to Know:
- Heart chambers: atria and ventricles
- Valves: mitral, tricuspid, aortic, and pulmonary
- Major vessels: aorta, coronary arteries, and veins
- Conduction system: SA node, AV node, and bundle of His
2. Musculoskeletal System: Bones, Joints, and Beyond
The musculoskeletal system encompasses bones, muscles, joints, ligaments, and tendons, and it’s another crucial area for coders. Whether coding for fractures, joint replacements, or muscle tears, a detailed understanding of this system is vital. Coders should be familiar with the major bones of the body, joint structures, and common musculoskeletal injuries and conditions.
Key Anatomy to Know:
- Major bones: femur, tibia, humerus, radius, ulna, and vertebrae
- Joints: shoulder, knee, hip, elbow, and vertebral
- Muscles: deltoid, biceps, quadriceps, and hamstrings
- Ligaments and tendons: ACL, PCL, Achilles tendon
3. Respiratory System: Breathing Life into Coding
The respiratory system is integral to many medical conditions, particularly in patients with chronic illnesses such as COPD and asthma. Coders need to understand the anatomy of the lungs, airways, and related structures to accurately code respiratory conditions and procedures like intubation, bronchoscopy, and thoracentesis.
Key Anatomy to Know:
- Airways: trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles
- Lungs: lobes, alveoli, and pleura
- Diaphragm: primary muscle of respiration
- Accessory muscles: intercostals and scalene muscles
4. Gastrointestinal System: The Pathway to Proper Coding
The gastrointestinal (GI) system, which includes the esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, and pancreas, is another area where anatomy knowledge is crucial. Accurate coding for conditions like GERD, ulcers, Crohn’s disease, and pancreatitis, as well as procedures such as endoscopy, colonoscopy, and gallbladder removal, requires an in-depth understanding of GI anatomy.
Key Anatomy to Know:
- Esophagus, stomach, and intestines (small and large)
- Accessory organs: liver, gallbladder, and pancreas
- GI tract layers: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, and serosa
- Sphincters: lower esophageal sphincter, pyloric sphincter
5. Nervous System: Understanding the Body’s Control Center
The nervous system, consisting of the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves, controls nearly every function in the body. Coders must be familiar with the central and peripheral nervous systems to accurately code neurological conditions like strokes, seizures, and neuropathies, as well as procedures such as lumbar punctures and craniotomies.
Key Anatomy to Know:
- Brain: cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, and lobes
- Spinal cord: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral segments
- Peripheral nerves: cranial nerves, spinal nerves, and plexuses
- Meninges: dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater
- Anatomic sites of the eyes and ears: optic nerve, retina, cochlea, and auditory nerve
6. Reproductive System: Essential Knowledge for Specialized Coding
For coders working in specialties like obstetrics, gynecology, or urology, an understanding of the reproductive system is indispensable. This includes knowing the anatomy of the female and male reproductive organs, as well as related structures like the breast, which are crucial for coding conditions like endometriosis, prostate cancer, and breast biopsies.
Key Anatomy to Know:
- Female reproductive organs: ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and cervix
- Male reproductive organs: testes, prostate, and seminal vesicles
- Breast anatomy: lobes, ducts, and areola
- Reproductive cycles: menstrual and spermatogenesis
7. Urinary System: Critical for Urological Coding
The urinary system, responsible for filtering and eliminating waste from the body, is a vital area of focus for coders, particularly those working in urology. Coders need to understand the anatomy of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra to accurately code for conditions such as kidney stones, UTIs, and renal failure, as well as procedures like cystoscopy, lithotripsy, and nephrectomy.
Key Anatomy to Know:
- Kidneys: cortex, medulla, nephrons
- Ureters: tubes transporting urine from kidneys to bladder
- Bladder: detrusor muscle, trigone area
- Urethra: passage for urine excretion
8. Integumentary System: Skin-Deep Coding Essentials
The integumentary system, which includes the skin, hair, nails, and associated glands, plays a significant role in coding for dermatological conditions and procedures. Coders should be familiar with the layers of the skin, types of lesions, and common conditions such as psoriasis, eczema, and skin infections, as well as procedures like biopsies, excisions, and wound care.
Key Anatomy to Know:
- Skin layers: epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue
- Skin appendages: hair follicles, sebaceous (oil) glands, and sweat glands
- Types of lesions: macules, papules, nodules, and ulcers
- Common skin conditions: dermatitis, acne, and fungal infections
Conclusion: The Importance of Anatomy in Medical Coding
Anatomy is fundamental to accurate medical coding. A thorough understanding of key anatomical structures enables coders to precisely interpret clinical documentation, assign the correct codes, and adhere to coding standards. This focus on anatomy not only boosts coding accuracy but also minimizes errors, enhancing the overall quality of healthcare delivery.
At HIAlearn.com, we offer an extensive range of medical coding courses that emphasize the anatomical aspects of coding to provide coders with a comprehensive understanding of their subjects. With over 200 courses available, we are equipped to expand your knowledge and skills in medical coding. Explore our offerings at HIAlearn.com and advance your proficiency today.
HIAlearn, powered by Health Information Associates (HIA)—a leader in medical coding and auditing for over 30 years—offers a comprehensive online education platform for medical coders. With a catalog of over 200 medical coding courses accepted by the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA) for Continuing Education Units (CEUs) and a selection accredited by the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC), HIAlearn caters to both beginners and experienced medical coders seeking to enhance their skills. The platform provides an array of training plans tailored to meet individual learning needs, from mastering challenging coding procedures to understanding broad conceptual frameworks within the coding world. Courses are available across various coding types including CPT, E/M, ICD-10-CM, ICD-10-PCS, and are designed to cater to different coder levels and coding specialties such as inpatient, outpatient, profee, and CDI. Additionally, HIAlearn offers a Coding Updates bundle to ensure coders are up-to-date with the annual changes in ICD-10-CM, ICD-10-PCS, CPT, and IPPS. Beyond individual learning, HIAlearn supports organizations with group discounts, promoting enhanced coding accuracy, efficiency, and compliance across teams. With over 1,600 users already part of the HIAlearn community, the platform stands as a testament to its commitment to providing quality education and support for medical coders nationwide.
The information contained in this blog post is valid at the time of posting. Viewers are encouraged to research subsequent official guidance in the areas associated with the topic as they can change rapidly.